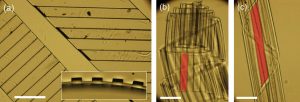
Optical microscopy images of example strips of bilayer films with thin parylene-C film deposited on the topographically patterned side of the PDMS. Scale bars: 300 mm. (a) Top-view of two dry bilayer strips with ridges at different angles. (Inset) Cross-sectional view of strip showing topographic pattern. (b, c) Swollen bilayer strips made from bilayer strips in (a) after immersion in hexadecane. The strip on the left in (a) transforms into a “tube roll” (b) after swelling. The strip on the right in (a) transforms into a “helical tube” (c) after swelling. Red shading is to guide the eye about representative ridges on the strip.
R. D. Kamien, S. Yang and A. G. Yodh
Building complex three-dimensional (3D) materials from pre-programmed two-dimensional films presents exciting challenges and opportunities. To achieve this goal, researchers inspired by the paper folding techniques of origami and kirigami have successfully utilized the mechanical instabilities of thin films, such as buckling.
This research study pushed beyond “flat films” and explored the role of topography in the swelling-induced buckling of bilayer films. To demonstrate the concept, we first created stripe patterns (by replica molding) on one-side of the swellable polymer (PDMS) film. Then a thin layer of non-swelling parylene was deposited uniformly onto the molded side of the PDMS. After swelling, the bilayer films buckle because of mismatched swelling ratios between the PDMS and parylene. Interestingly, simple topographic patterns on the bilayer film (like stripes) can lead to novel 3D structures, including half-pipes, helical tubules, and ribbons, all controlled via a few physical constraints.
The new research helps us better understand the role of topography in mechanical instabilities and introduces a simple method to harness instabilities to create desired 3D structures.
Jeong, Cho, Lee, Gong, Kamien, Yang, and Yodh, Topography-guided buckling of swollen polymer bilayer films into three-dimensional structures. Soft Matter 13, 956-962 (2017)
